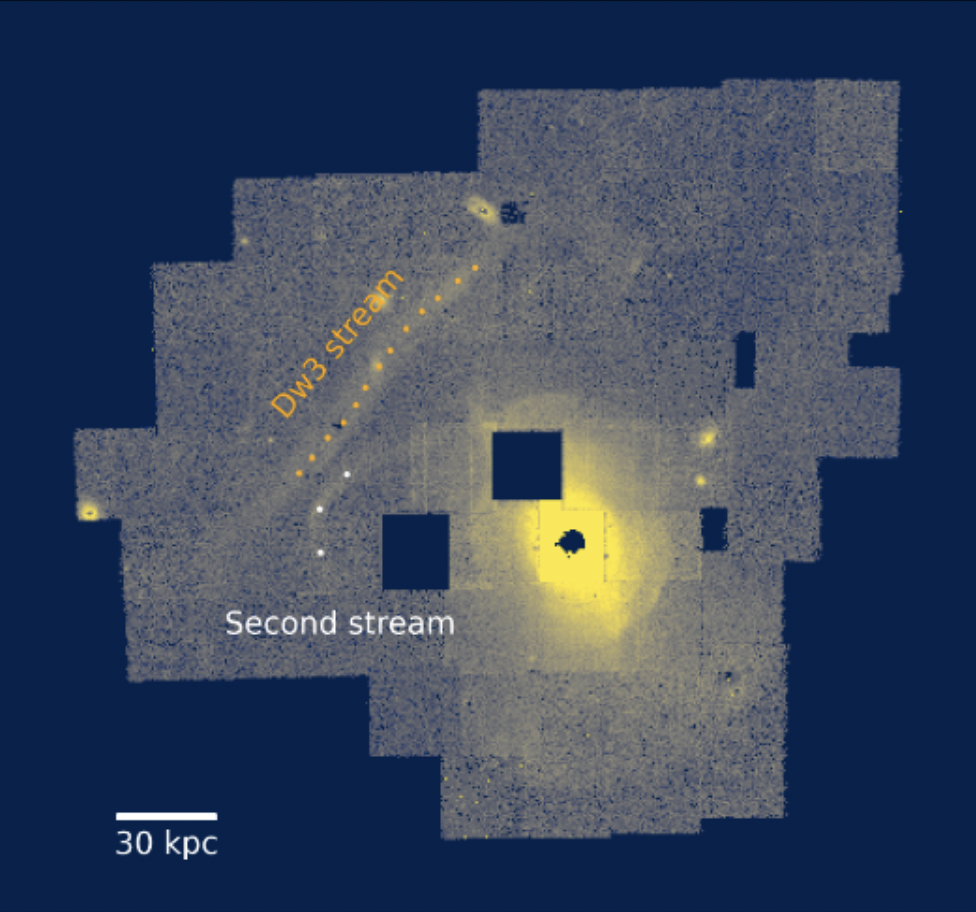
 -Centaurus A's stellar streams, Pearson et al. 2022b
-Centaurus A's stellar streams, Pearson et al. 2022b Academic career
Sarah has published scientific papers [see ADS link] in numerous journals, and her science covers topics such as galactic collisions, stellar streams, stellar explosions and dark matter. Her publications have been cited more than 600 times, and she has given invited talks at Harvard, MIT, the Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton and several other institutions. She has also won awards for her research, e.g. the Danish Women in Physics Prize, and she has mentored nine different students on a broad range of research topics.Biography
Sarah obtained her Bachelor’s degree in Physics from the University of Copenhagen in 2012, after which she acquired her Master’s and PhD degrees in Astronomy from Columbia University in 2015 and 2018, respectively. Currently, she holds a NASA Hubble Fellowship at New York University, where she studies galactic dynamics, dark matter and galactic bars. Prior to to this, Sarah held a Flatiron Research Fellowship at the Center for Computational Astrophysics.
Research interests
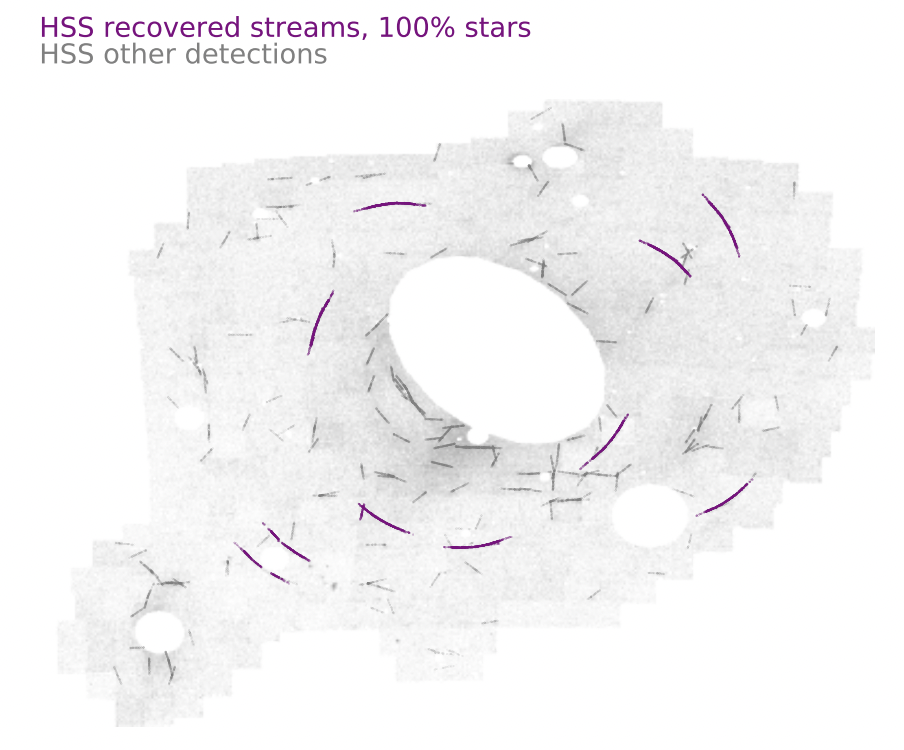 - Pearson et al. 2022aStellar streams
- Pearson et al. 2022aStellar streams
Stellar streams form when tidal forces from galaxies tear smaller stellar systems apart into streak-like structures that persist for billions of years. Sarah's work focuses on stellar streams beyond the Milky Way and what they can teach us about dark matter. In Pearson et al. (2022b), she developed a novel extragalactic stream-fitting technique and used the straight stream near Centaurus A (Cen A), to place limits on Cen A's dark matter halo mass. In Pearson et al. (2019), Sarah and her collaborators demonstrated that thin stellar streams from globular cluster will be observable in at least 200 nearby galaxies with NASA's Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope, and in Pearson et al. (2022a), she developed the "Hough Stream Spotter" code to find these thin streams in external galaxies. These thin extragalactic streams can hopefully help in the quest for the nature of dark matter, which Sarah is exploring with PhD student, C. Aganze, in (Aganze, Pearson et al. 2023).
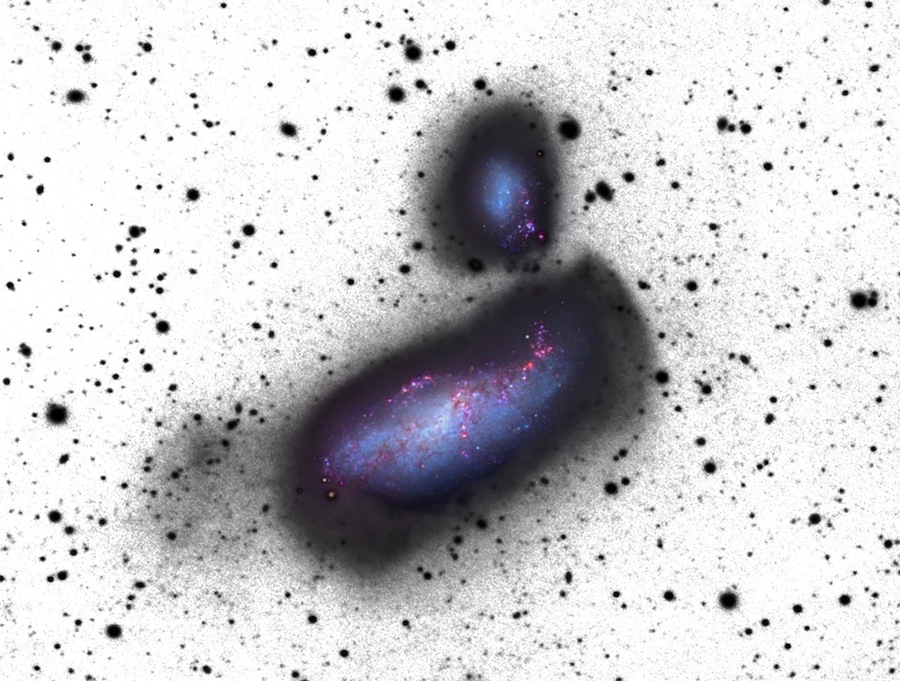 - Pearson et al. 2018Colliding galaxies
- Pearson et al. 2018Colliding galaxies
Sarah has been involved in observational (Pearson et al. (2016), Privon, Pearson+ 2017, Luber, Pearson+ 2022) and theoretical (Pearson et al. 2018, Besla, Pearson+ 2018) studies on the nature of collisions between dwarf galaxies. The motivation for investigating this population of galaxies, is to better understand how galaxies build up their mass in the early Universe, and how they cycle through their baryons.
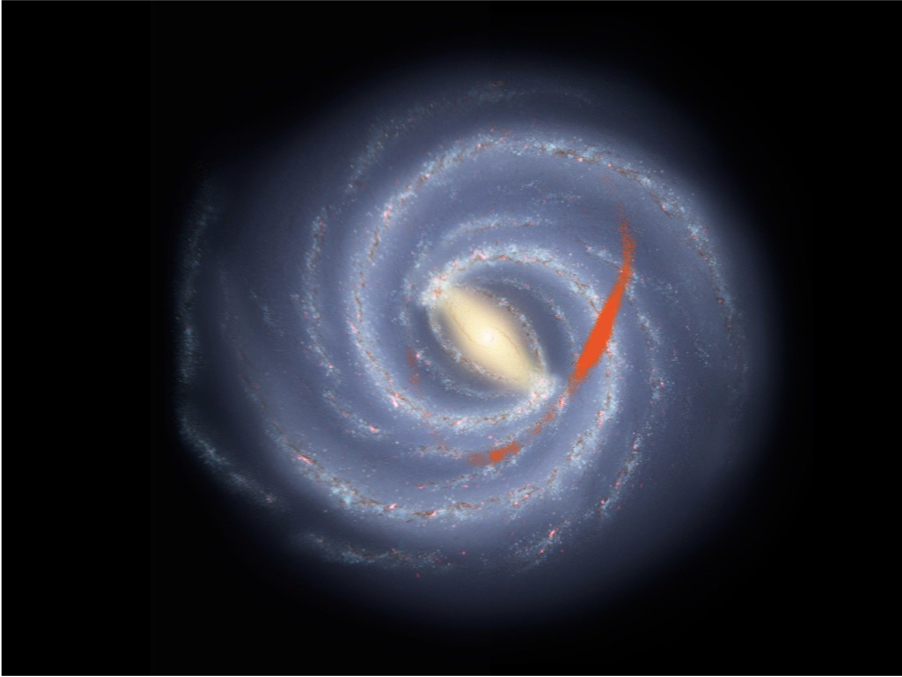 - Pearson et al. 2017The Galactic Bar
- Pearson et al. 2017The Galactic Bar
Sarah is also interested in galactic bars. In her Pearson et al. (2017) publication in Nature Astronomy, she showed that bars induce gaps in stellar streams similar to gaps induced by dark matter subhalos. She has since worked on several projects related to understanding the formation and evolution of galactic bars (see e.g. Ansar, Pearson et al. 2023, Lucey, Pearson et al. 2022, Bonaca, Pearson et al. 2020).
Scientific journal articles
First & second author [ADS link]
25. Prospects for Detecting Gaps in Globular Cluster Stellar Streams in External Galaxies with the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope
Aganze, C., Pearson, S., Starkenburg, T., Contardo, G. et al. 2023, submitted to AAS journals, arXiv: 2305.12045
24. Mapping Dark Matter with Extragalactic Stellar Streams: the Case of Centaurus A
Pearson, S., Price-Whelan, A., Hogg, D. et al. 2022b, ApJ, 941, 19, 17, arXiv: 2205.12277
23. Constraining the length and pattern speed of the Milky Way bar from direct orbit integration of APOGEE and Gaia data
Lucey, M., Pearson, S., Hunt, J. et al. 2023, MNRAS, 520, 3, 4779, arXiv: 2206.01798
22. Bar formation and destruction in the FIRE2 simulations
Ansar, S., Pearson, S., Sanderson, R. et al. 2022, submitted to AAS journals
21. Walter: A Tool for Predicting Resolved Stellar Population Observations with Applications to the Roman Space Telescope
Lancaster, L., Pearson, S., Williams, B. et al. 2022, AJ, 164, 4, 142, arXiv: 2207.02208
20. Investigating the Baryon Cycle in Interacting Dwarfs with the Very Large Array and Pan-STARRS
Luber, N., Pearson, S., Putman, M. E., Besla, G. et al. 2022, AJ, 163, 49 arXiv: 2111.04795
19. The Hough Stream Spotter: A new method for detecting linear structure in resolved stars and application to the stellar halo of M31
Pearson, S., Clark, S. E., Dimirjian, A. J., Johnston, K. V. et al. 2022, ApJ, 926, 166 arXiv: 2107.00017
18. Variations in the width, density, and direction of the Palomar 5 tidal tails
Bonaca, A., Pearson, S., Price-Whelan, A. et al. 2020, ApJ, 889, 70, arXiv: 1910.00592
17. Detecting Thin Stellar Streams in External Galaxies: Resolved Stars & Integrated Light
Pearson, S., Starkenburg, T., Johnston, K. V., Williams., B., and Ibata., R., 2019, accepted to ApJ, arXiv: 1906.03264
16. Modeling the Baryon Cycle in Dwarf Galaxy Encounters: the Case of NGC4490 & NGC4485
Pearson, S., Privon, G., Besla, G., Putman, M. E., Martinez-Delgado, D., Johnston, K. V., Gabany,
J. R., Patton, D. R., Kallivayalil, N. 2018, MNRAS, 480, 3069, arXiv: 1807.03791
15. Gaps and Length Asymmetry in the Stellar Stream Palomar 5 as Eects of Galactic Bar Rotation
Pearson, S., Price-Whelan, A. M., Johnston, K. V. 2017, Nature Astronomy, 1, 9 arXiv: 1703.04627
14. Local Volume TiNy Titans: Gaseous Dwarf-Dwarf Interactions in the Local Universe
Pearson, S., Besla, G., Putman, M. E., Lutz, K., Fernandez, X., Stierwalt, S., Patton, D. R. et al.
2016, MNRAS, 459, 1827, arXiv: 1603.09342
13. Tidal Stream Morphology as an Indicator of Dark Matter Halo Geometry: the Case of Palomar 5
Pearson, S., Kupper, A. H. W., Johnston, K. V., A. M. Price-Whelan, 2015, ApJ, 799, 1, arXiv: 1410.3477
12. Unraveling the Origin of Overionized Plasma in the Galactic Supernova Remnant W49B
Lopez, L. A., Pearson, S., Ramirez-Ruiz, E., Castro, D., Yamaguchi, H., Slane, P., Smith, R. 2013,
ApJ, 764, 50, arXiv: 1309.1464
Other journal articles
11. New Velocity Measurements of NGC 5128 Globular Clusters out to 130 kpc: Outer Halo Kinematics, Substructure and Dynamics
Hughes, Sand, [9 auhors], Pearson, S., [3 authors], 2023, ApJ, 947, 34, arXiv: 2208.08997
10. Stream Fanning and Bifurcations: Observable Signatures of Resonances in Stellar Stream Morphology
Yavetz, T., Johnston, K. V., Pearson, S., Price-Whelan, A. et al., 2022, submitted to ApJ, arXiv: 2212.11006
9. Once in a Blue Stream: Detection of Recent Star Formation in the NGC 7241 Stellar Stream with MEGARA
Martinez-Delgado, D., [8. authors], Pearson, S., [16. authors], 2021, submitted to MNRAS, arXiv: 2112.07029
8. Hidden Depths in the Local Universe: the Stellar Stream Legacy Survey
Martinez-Delgado, D., [4. authors], Pearson, S., [17. authors], 2023, AA, 671, 14, arXiv: 2104.06071
7. Separatrix Divergence of Stellar Streams in Galactic Potentials
Yavetz, T., Johnston, K. V., Pearson, S., Price-Whelan, A., Weinberg, M., 2021, MNRAS, 501, 1791, arXiv: 2011.11919
6. Kinematics of the Palomar 5 stellar stream from RR Lyrae stars
Price-Whelan, A., Mateu, C., Iorio, G., Pearson, S., Bonaca, A., Belokurov, V., 2019, AJ, 158, 223, arXiv: 1910.00595
5. The Frequency of Dwarf Galaxy Multiples at Low Redshift in SDSS vs. Cosmological Expectations
Besla, G., Patton, D. R., Stierwalt, S., Rodriguez-Gomez, V., Patel, E., Kallivayalil, N. J., Johnson, K. E., Pearson, S., Privon, G. C.; Putman, M. E., 2018, MNRAS, 480, 3376, arXiv: 1807.06673
4. A Widespread, Clumpy Starburst in the Ongoing Isolated Dwarf Galaxy Merger DM1647+21
Privon, G., Stierwalt, S., Patton, D. R., Besla, G., Pearson, S., Putman, M., Johnson, K. E., Kallivayalil, N., Liss, S., 2017, ApJ, 846, 74, arXiv: 1708.02587
3. Evidence of Fanning in the Ophiuchus Stream
Sesar, B., Price-Whelan, A. M., Cohen, J. G., Rix, H. W., Pearson, S., Johnston, K. V., Bernard, E. J., Ferguson, A. M. N., Martin, N. F., Slater, C. T., Chambers, K. C., Flewelling, H., Wainscoat, R. J., Waters, C., 2016, ApJL, 816, 1, L4, arXiv: 1512.00469
2. Chaotic Dispersal of Tidal Debris
Price-Whelan, A., Johnston, K. V., Valluri, M., Pearson, S, Küpper, A. H. W., Hogg, D. W., 2016, MNRAS, 455, 1079, arXiv: 1507.08662
1. The Galactic Supernova Remnant W49B Likely Originates from a Jet-Driven Core-Collapse Explosion
Lopez, L. A., Ramirez-Ruiz, E., Castro, D., Pearson, S. 2013, ApJ, arXiv: 1301.0618